Don’t Let Hail Hide: Why Your TPO Roof Needs an Expert Post-Storm Inspection
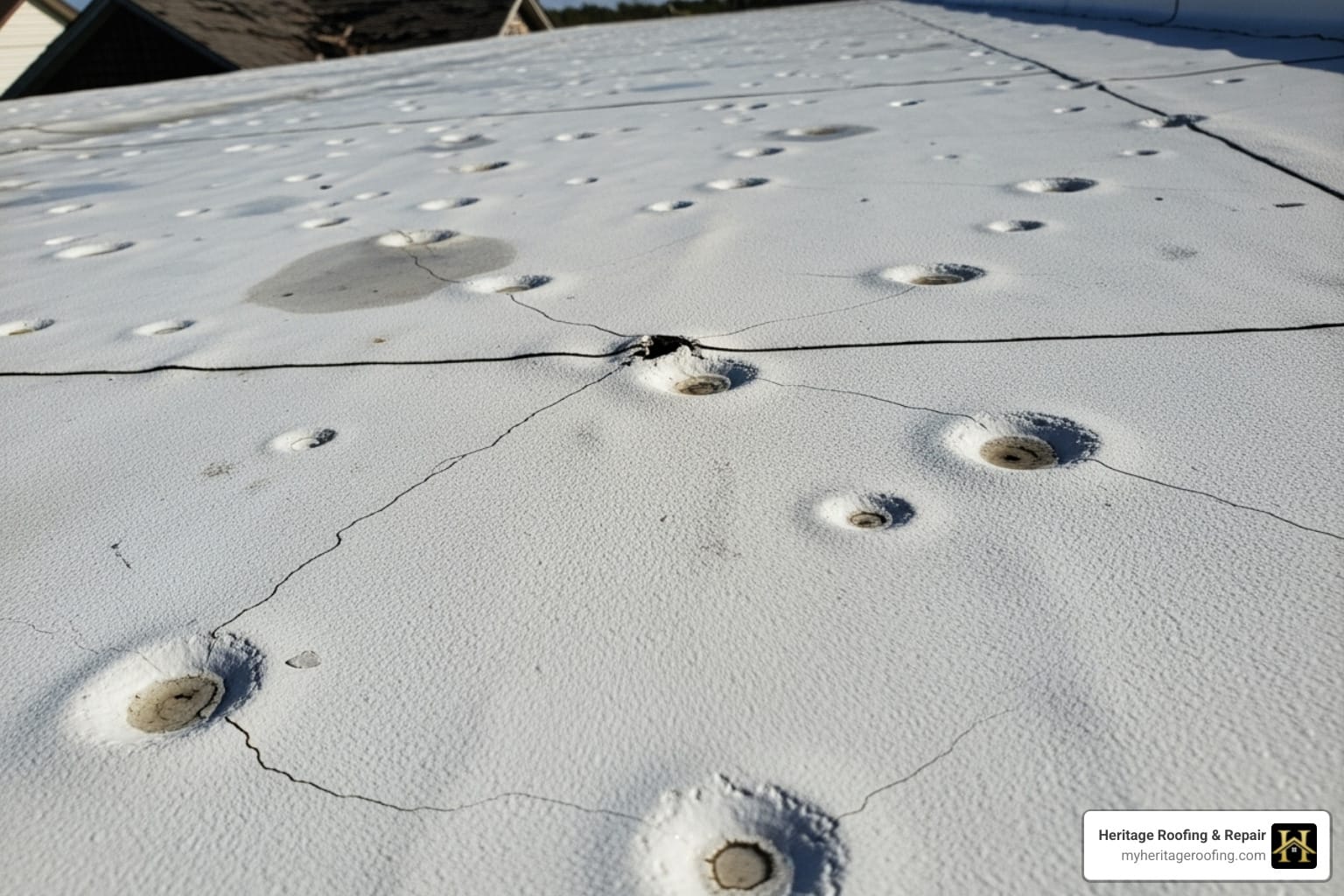
TPO roofing hail damage can be deceptive. What appears as minor surface scuffs can hide significant, underlying issues that compromise your building’s integrity. After a storm, a professional inspection is crucial. As the leading provider of commercial roofing services in Northwest Arkansas, we’ve seen firsthand how undetected hail damage leads to costly, long-term problems. While TPO is a durable choice, it’s not invincible against the severe hailstorms common to our region, making a post-hail check-up essential for every property owner.
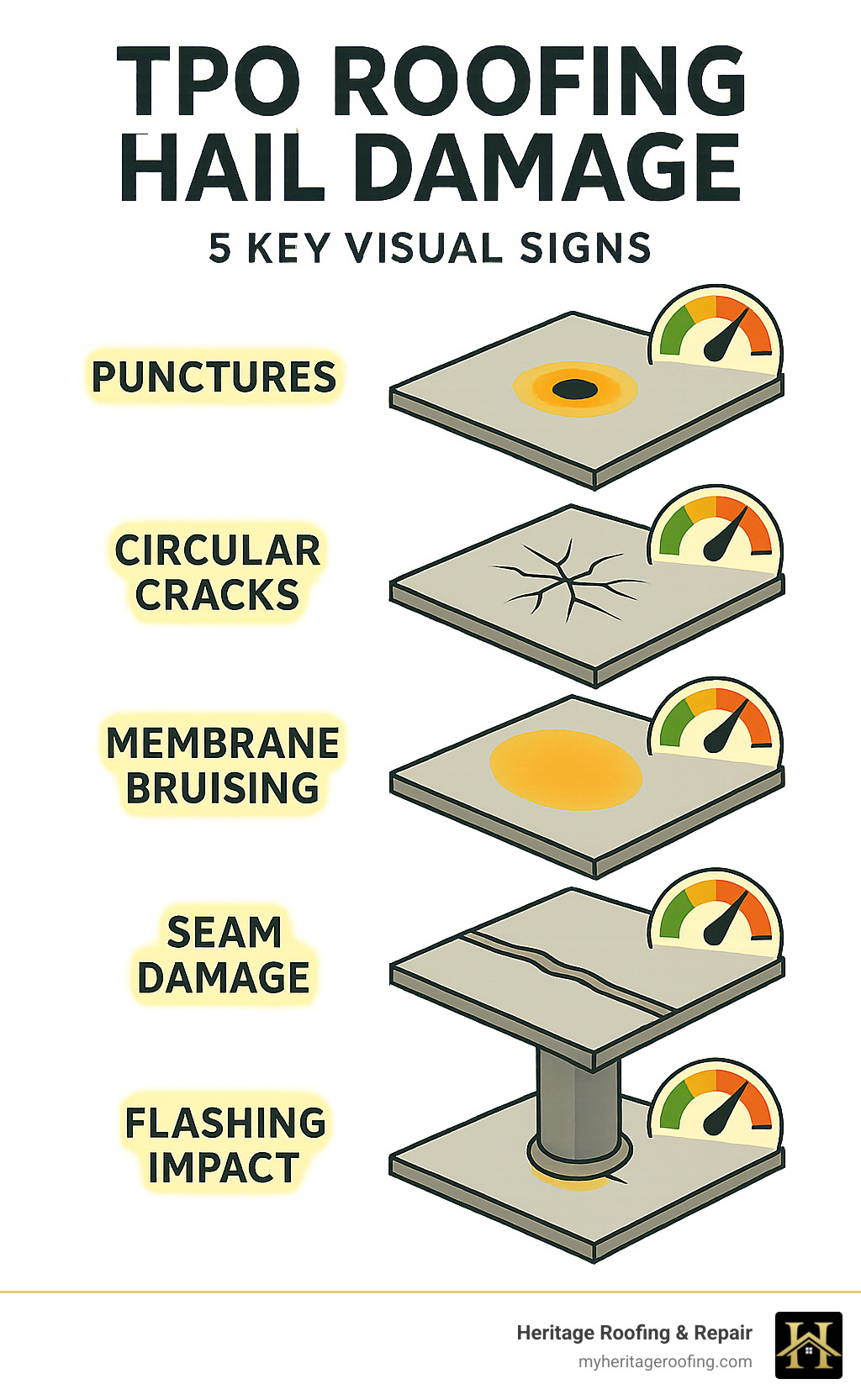
Key signs of TPO hail damage to look for:
- Visible punctures or circular cracks in the membrane
- Semicircular patterns or star-shaped damage
- Bruising or dents on the surface indicating compromised insulation
- Blisters or membrane delamination
- Weakened seams or membrane shrinkage
- Damage to flashing and roof penetrations
TPO membranes can resist damage from hailstones up to 1 3/4 inches in diameter, but larger stones – or repeated impacts from smaller ones – can cause significant problems. Research shows that while hail-caused dents rarely affect insulation R-value by more than 2%, punctures and cracks create serious risks for water infiltration and structural damage.
The challenge with TPO hail damage is that the most serious problems aren’t always visible from ground level. What appears as minor surface denting may actually indicate damaged underlying insulation, compromised seam integrity, or weakened membrane areas that will fail over time.
I’m Rex Wisdom, owner of Heritage Roofing & Repair, and in over 50 years of serving Northwest Arkansas, I’ve seen how quickly undetected TPO roofing hail damage can escalate into costly structural repairs. Understanding the signs early and taking swift action is crucial for protecting your commercial property investment.
Spotting the Unseen Enemy: How to Identify Hail Damage on TPO Roofs
After a hailstorm, the first thing on every property owner’s mind is, “Is my roof okay?” When it comes to TPO roofs, the answer isn’t always as simple as a quick glance. While TPO (Thermoplastic Polyolefin) is a robust single-ply membrane known for its durability and energy efficiency, it’s not immune to the fury of a hailstorm. Identifying tpo roofing hail damage requires a keen eye and understanding of what to look for.
The common types of hail damage observed on TPO roofs can range from obvious punctures to subtle, insidious signs that hint at underlying issues. Property owners should be on the lookout for both direct impact signs and more discreet indicators. For more detailed insights into TPO systems, visit our TPO Roofing page.
To conduct a thorough inspection, we recommend having a few simple tools on hand:
- Sturdy ladder for safe roof access
- Non-slip shoes to maintain footing on the membrane
- Camera (your phone works great!) for documenting damage
- Notebook and pen for jotting down observations
- Chalk to circle and mark damaged areas for repair or further inspection
Telltale Visual Signs of Direct Hail Impact
When hailstones directly strike a TPO roof, they can leave immediate and unmistakable marks. These are often the first signs property owners notice:
- Visible punctures: These are holes where hailstones have completely penetrated the TPO membrane. Larger hailstones, especially jagged ones, are the culprits here. These are red flags for immediate water infiltration.
- Circular or star-shaped cracks: Hail impact can cause the membrane to crack in a distinct circular or star pattern without fully puncturing it. This indicates a compromise in the membrane’s integrity, which can lead to splits and leaks over time.
- Blisters or delamination: The force of impact can cause the TPO membrane to separate from the underlying layers (like insulation or adhesive), creating raised blisters. This delamination weakens the roof and can lead to tears.
- Obvious dents in the membrane: Even if the membrane isn’t punctured, hail can leave noticeable depressions or indentations. While seemingly cosmetic, these dents can signal damage to the insulation below.
- Damage to flashing and vents: Don’t forget the details! Hail can ding, crack, or dislodge flashing around vents, skylights, and parapet walls, creating pathways for water.
Subtle Indicators of Compromised TPO Roofing Hail Damage
Sometimes, the most serious damage isn’t immediately obvious. It’s the subtle signs that often reveal long-term problems. These less apparent indicators can be easily missed but are crucial for a comprehensive assessment:
- Membrane shrinkage or pulling at seams: Hail impacts, combined with thermal stress, can exacerbate existing weaknesses. If you see the membrane pulling away from seams or flashing, or if seams appear stretched and thin, it could be a sign of underlying hail-induced stress or material degradation.
- Bruising without punctures: This is where the TPO membrane looks discolored or has soft spots, even without a visible hole. This “bruising” indicates that the membrane’s internal structure has been compromised, reducing its elasticity and making it prone to future cracking.
- Weakened or failing seam welds: TPO roofs rely on heat-welded seams for watertight integrity. Hail impact, even if not directly on the seam, can transfer energy that stresses the seam, leading to micro-cracks or bond failure that might not be visible until water starts to seep through.
- Damage to underlying insulation felt through the membrane: This is a critical sign. If you feel soft spots or crunching underfoot on the TPO membrane, it could mean the underlying insulation board has been dented, fractured, or crushed by hail. This can lead to loss of R-value and create voids where water can collect.
Need local help fast in Northwest Arkansas? You can reach Heritage Roofing & Repair here:
Heritage Roofing & Repair
3458 Arkansas State Hwy 221, Berryville, AR 72616
(870) 654-1164
Beyond the Surface: The Full Impact of TPO Roofing Hail Damage
The effects of tpo roofing hail damage extend far beyond what you see on the surface. While punctures and cracks are immediate concerns for leaks, the long-term implications for your roof’s structural integrity and longevity can be far more costly. Unaddressed damage can lead to a cascade of problems, impacting everything from your building’s energy efficiency to its very foundation. If your roof has suffered from a storm, it’s critical to have it professionally assessed to prevent further issues.
The primary concern with any roof damage is water infiltration. Even small, seemingly insignificant hail impacts can create micro-fractures that allow water to slowly seep into the roofing system. This leads to:
- Mold growth: Moisture trapped within the roof assembly creates a perfect breeding ground for mold, which can spread into the building’s interior, causing health issues and requiring expensive remediation.
- Insulation damage: Wet insulation loses its thermal properties, leading to energy loss.
- Structural integrity compromise: Persistent water leaks can rot wooden decking, corrode metal components, and weaken the overall structural integrity of your roof, potentially leading to costly repairs or even premature roof replacement.
- Longevity reduction: Even if immediate leaks aren’t apparent, hail damage accelerates the aging process of the TPO membrane, significantly shortening its expected lifespan.
Does Hail-Caused Denting Affect Your Insulation’s R-Value?
This is a question we hear often, and it’s a valid concern for property owners focused on energy efficiency. The R-value of roof insulation is a measure of its resistance to heat flow, directly impacting your building’s heating and cooling costs. If hail dents the insulation beneath your TPO membrane, does it reduce this critical R-value?
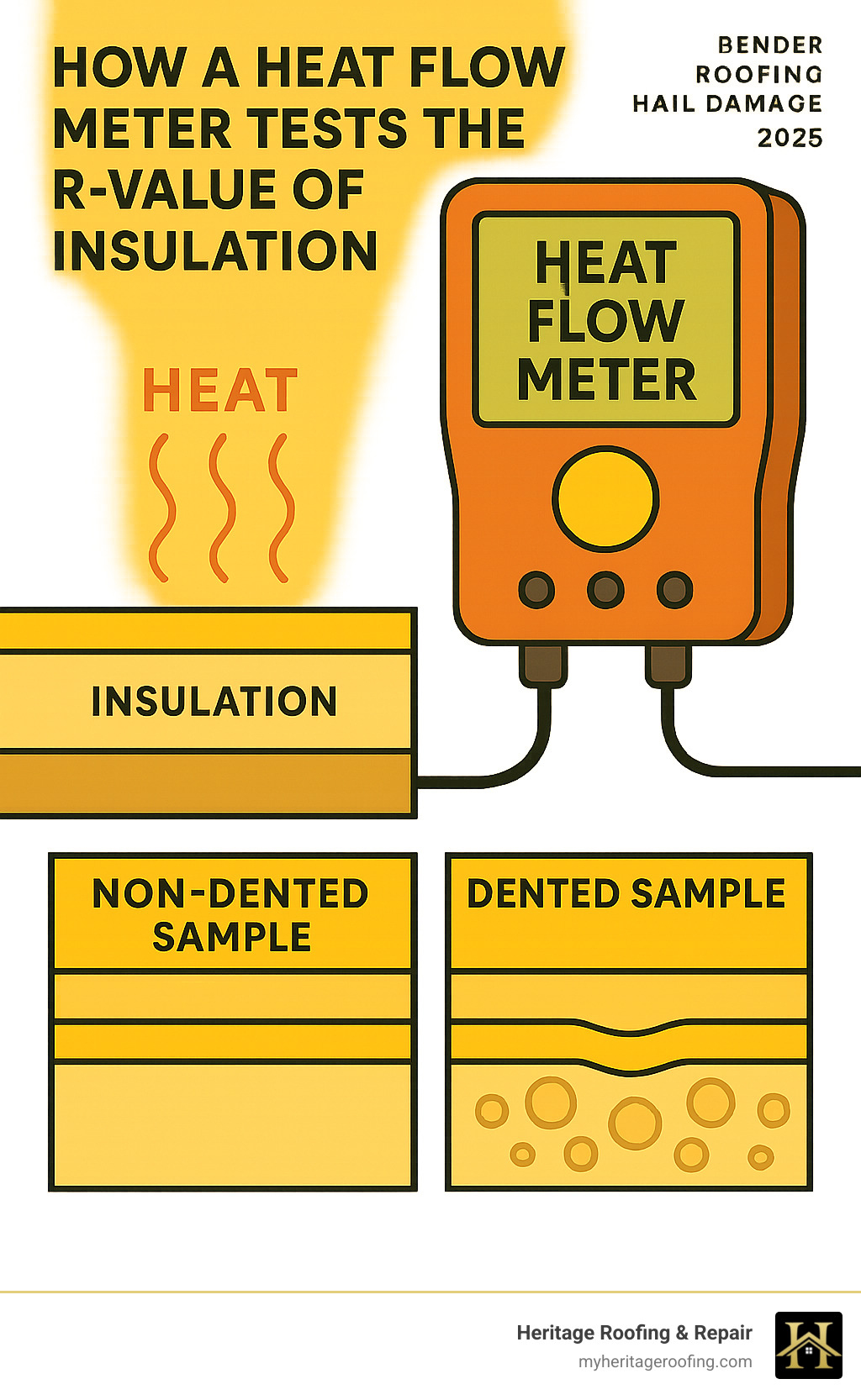
According to research from Haag Global, the answer is often “not significantly.” Their studies, using a heat flow meter (HFM) and adhering to ASTM C518 and ASTM C1058 standards, found that hail-caused dents in TPO roofing insulation, even at high frequencies (simulating 900 dents/sq ft, far more than typically seen in the field), had no measurable effect on the R-value within the accuracy of the testing equipment (+/- 2%). A scientific look at hail-dented insulation confirms this.
This is good news! It suggests that cosmetic dents alone might not be a major cause for concern regarding energy performance. However, there’s a crucial caveat: if dents are sufficiently large, deep, or numerous, a subtle change in R-value can be measured. More importantly, if hail causes the insulation to crack or rupture, creating “thermal shorts” (direct paths for heat to escape), then the R-value will be significantly impacted. The real threat to R-value isn’t just the dent, but the potential for the dent to become a pathway for moisture or to severely damage the insulation’s structure. Water-soaked insulation, for instance, loses almost all its thermal resistance.
How Hail Damage Compromises Your Roof’s Longevity and Structure
Beyond immediate leaks and potential R-value concerns, tpo roofing hail damage systematically undermines the long-term health of your roof:
- Accelerated aging: Every impact site, even if not immediately leaking, is a point of stress. These micro-fractures and weakened areas become more susceptible to the daily expansion and contraction caused by temperature changes, leading to premature cracking and material fatigue.
- UV degradation at impact sites: TPO is designed to resist UV radiation, but hail impacts can displace the protective top layer or expose the underlying scrim. These exposed areas are then more vulnerable to UV degradation, which can make the membrane brittle and prone to further damage.
- Compromised seams leading to leaks: TPO seams are heat-welded for strength. Hail impacts, even near seams, can weaken these crucial bonds. Over time, these compromised seams can begin to pull apart, creating insidious leak paths that are difficult to detect until water stains appear inside your building.
- Saturated insulation losing structural support: When water infiltrates due to hail damage, it saturates the insulation. Wet insulation not only loses its thermal value but also its structural integrity. It can become soft, squishy, or even collapse, creating voids and uneven surfaces on the roof, which can lead to ponding water and further deterioration.
- Potential for deck rot or corrosion over time: Water that bypasses the membrane and insulation eventually reaches the roof deck. For wood decks, this means rot and decay. For metal decks, it means corrosion. Both scenarios can severely compromise the structural integrity of your entire roof system, leading to very expensive, extensive repairs or even a full roof replacement.
TPO vs. The Competition: A Hail Resistance Showdown
When considering how well a roof will stand up to nature’s fury, especially hailstorms, it’s helpful to compare different materials. TPO is a popular choice, but how does it truly stack up against other common flat roofing materials like EPDM and Modified Bitumen?
The age and condition of a TPO roof significantly affect its susceptibility to hail damage. An older roof, particularly one with initial TPO formulations known to fail prematurely (some as early as 5 to 16 years), will naturally be more prone to damage than a newer, well-maintained one. Factors like UV exposure, ponding water, and even manufacturing defects can accelerate deterioration, making the roof’s defense against hail much weaker.
How TPO Stacks Up Against Other Flat Roofing Materials
Each flat roofing material has its own strengths and weaknesses when it comes to hail resistance:
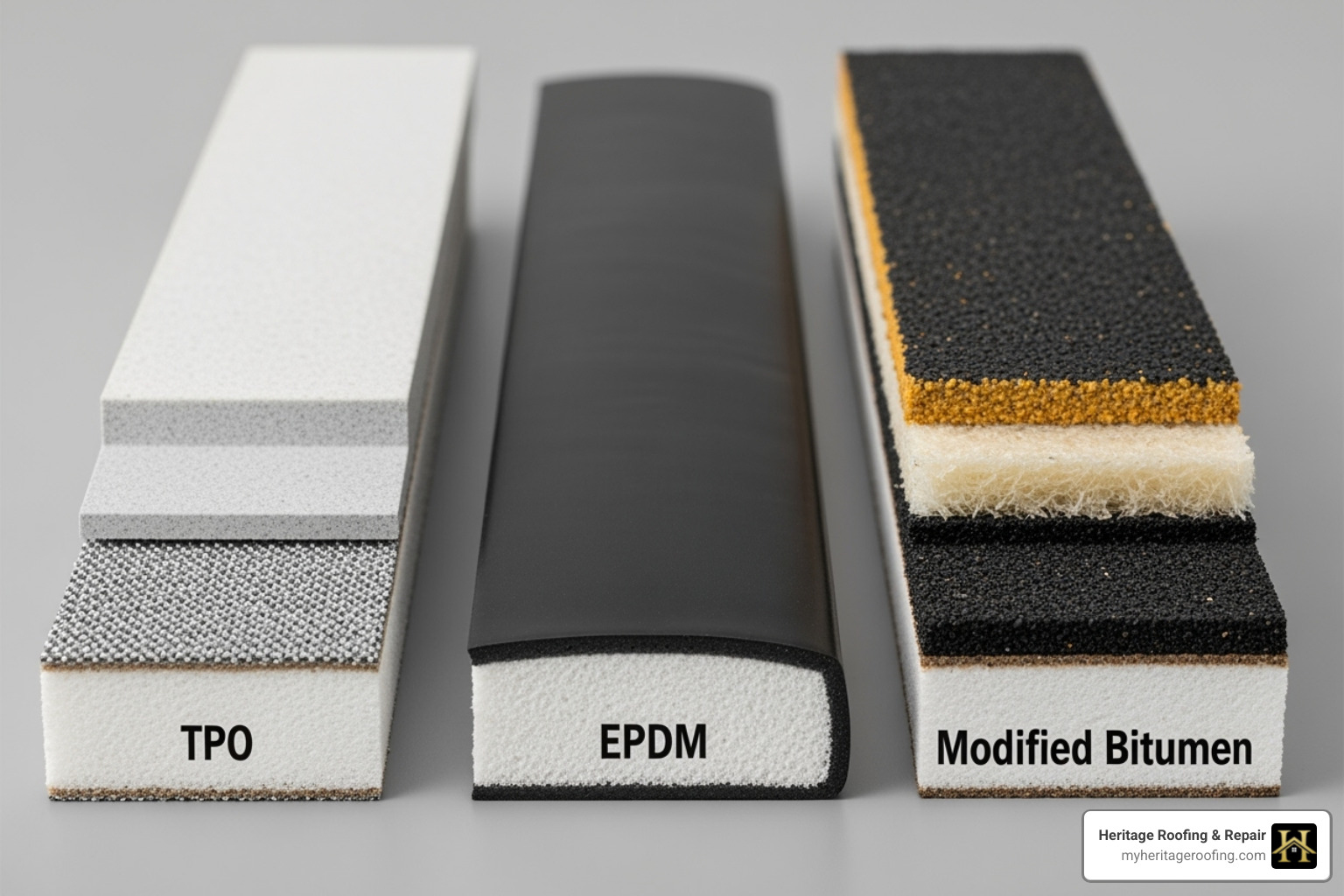
- TPO (Thermoplastic Polyolefin): TPO membranes can resist damage from up to 1 3/4-inch hailstones. While this might seem modest, TPO’s inherent flexibility allows it to absorb and dissipate impact energy relatively well, making it generally more hail-resistant than smooth surface built-up roofs.
- EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer): EPDM roof membranes can resist damage from up to 2 1/2-inch hailstones. While EPDM can withstand larger hailstones, it can sometimes be less flexible than TPO upon impact, potentially leading to cracks or splits, especially as it ages.
- Modified Bitumen: Modified bitumen roofs may crack or tear under severe hail, especially if the surface granules are displaced. BUR membranes are more susceptible to damage from small hailstones, usually about 1 1/2 inches in diameter.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Material | Typical Hail Resistance | General Performance |
|---|---|---|
| TPO | Up to 1 3/4″ stones | Good flexibility, absorbs impact well |
| EPDM | Up to 2 1/2″ stones | Handles larger stones but can become brittle |
| Modified Bitumen | ~1 1/2″ stones | Vulnerable to granule loss and UV exposure |
What are the common types of hail damage observed on TPO roofs?
Hail damage on TPO roofs can manifest in several ways, from obvious physical breaches to subtle structural compromises. The most common types include:
- Punctures and Tears: These are direct breaches in the membrane caused by larger, sharper hailstones. They create immediate pathways for water.
- Cracks (Spider Cracks or Radial Fractures): Hail impact can cause the TPO membrane to crack in a circular or star-shaped pattern around the point of impact. These may not immediately leak but compromise the membrane’s integrity.
- Bruising or Dents: These appear as depressions or discolorations on the membrane surface. While the membrane itself might not be ruptured, these dents indicate impact force that can damage the underlying insulation.
- Blistering and Delamination: The impact can weaken the adhesion between the TPO membrane and the substrate, leading to air pockets (blisters) or separation (delamination).
- Weakened Seams: Even if not directly hit, hail impacts can stress the heat-welded seams, leading to micro-fractures or reduced bond strength, which can eventually fail and cause leaks.
- Granule Loss (on older, granulated TPO): Some older TPO formulations had a granulated surface, similar to modified bitumen. Hail can dislodge these granules, exposing the membrane to UV degradation.
How does the age and condition of a TPO roof affect its susceptibility to hail damage?
The age and overall condition of a TPO roof play a significant role in its ability to withstand hail. A newer, well-installed TPO roof will naturally be more resilient than an older, degraded one.
- Aging and Material Degradation: As TPO membranes age, they can lose their plasticizers and become more brittle. This reduced flexibility makes them more susceptible to cracking and tearing from hail impacts. Some initial TPO formulations, especially those from the early 2000s, were known to fail prematurely, sometimes in as little as 5 to 16 years, due to material degradation. This means an older TPO roof, even if seemingly fine, could be a ticking time bomb when a hailstorm hits.
- UV Exposure: Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation breaks down the TPO material, reducing its elasticity and making it more prone to damage. Hail impacts on UV-degraded areas can cause more severe, widespread cracking.
- Ponding Water: Areas of a TPO roof where water consistently pools (ponds) can experience accelerated deterioration. This “microwave effect” from water and UV can weaken the membrane, making it highly vulnerable to hail.
- Pre-existing Damage or Poor Installation: A roof that already has minor membrane damage, compromised seams, or was poorly installed (e.g., inadequate substrate, incompatible materials) will have a significantly lower resistance to hail impacts. For example, laying TPO over an old tar roof without a proper separation layer can cause early deterioration due to off-gassing.
What are the signs of hail damage on a TPO roof that property owners should look for?
Identifying tpo roofing hail damage requires a thorough inspection, looking for both obvious and subtle clues. As we discussed in the intro, here are the key signs:
Telltale Visual Signs of Direct Hail Impact
These are often the most noticeable and indicate direct physical force from hailstones:
- Visible punctures: Look for clear holes, ranging from pinpricks to larger gashes, where hailstones have breached the membrane.
- Circular or star-shaped cracks: These are fractures in the membrane that radiate outwards from an impact point. They might not go all the way through initially but will worsen over time.
- Blisters or delamination: Raised bubbles or areas where the membrane has separated from the underlying layers.
- Obvious dents in the membrane: Depressions or indentations on the surface, which can indicate damage to the insulation below.
- Damage to flashing and vents: Check metal flashing, pipe boots, skylight curbs, and other roof penetrations for dings, cracks, or displaced components.
Subtle Indicators of Compromised TPO Roofing Hail Damage
These signs are less obvious but can point to significant underlying problems:
- Membrane shrinkage or pulling at seams: TPO naturally expands and contracts, but hail stress can exacerbate this, causing the membrane to pull excessively at seams or around penetrations.
- Bruising without punctures: Discolored, softened, or “spongy” areas on the membrane where the internal structure has been compromised without a full breach. This reduces the membrane’s flexibility and strength.
- Weakened or failing seam welds: Micro-cracks or separation along heat-welded seams, which may not be immediately apparent but allow for slow water infiltration.
- Damage to underlying insulation felt through the membrane: This is crucial. If you feel soft, crunchy, or uneven spots when walking on the roof, it indicates the insulation board beneath has been dented or fractured. A large enough hailstone (2″+) can cause the insulation to divot and break its fiberglass facer, leading to delamination and loss of adhesion, even if the TPO membrane itself isn’t visibly punctured. This can lead to significant energy loss and create voids for water.
Beyond the Surface: The Full Impact of TPO Roofing Hail Damage
Does Hail-Caused Denting Affect Your Insulation’s R-Value?
This is a common concern for property managers. The R-value measures an insulation’s thermal resistance, directly impacting your building’s energy efficiency. When hailstones dent the underlying insulation beneath a TPO membrane, does it reduce this critical R-value?
According to research by Haag Global, the impact of hail-caused dents on the R-value of roof insulation is often minimal. Their tests, which involved creating high frequencies of dents (up to 900 dents per square foot, much higher than typically observed in the field) on polyisocyanurate (polyiso) insulation, showed that the measured differences in R-value fell within the accuracy of their testing equipment (+/- 2%). For most hail-caused dents, there was no measurable effect on the R-value.
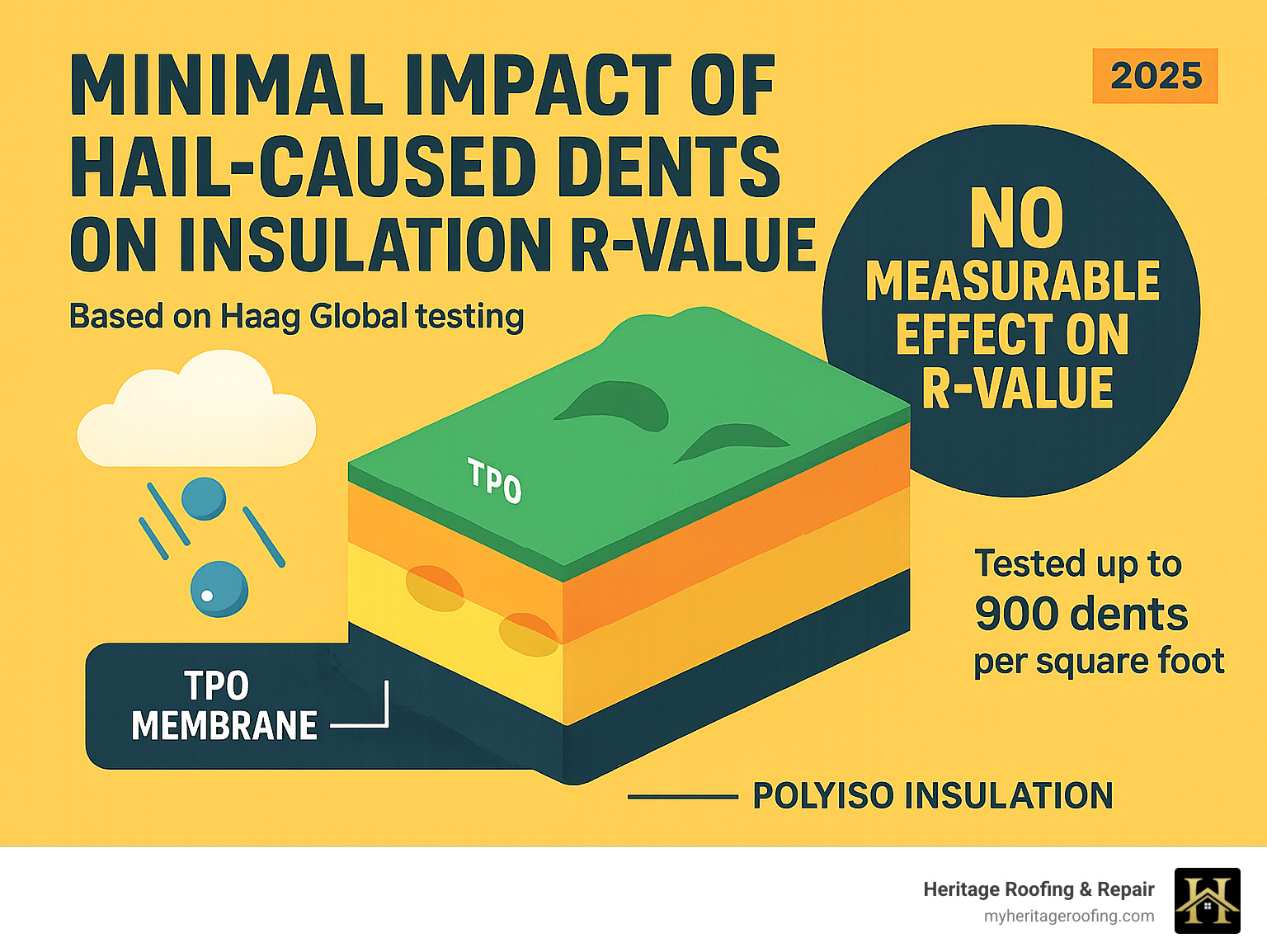
This is reassuring news, but it comes with important caveats:
- Punctures and Cracks are the Real Threat: While simple dents may not affect R-value, if hail leads to actual cracking or rupturing of the insulation, it creates “thermal shorts” – direct pathways for heat to escape – which will significantly impact R-value.
- Water-Soaked Insulation: The biggest threat to insulation’s R-value isn’t the dent itself, but water ingress. If hail damage to the TPO membrane allows water to saturate the underlying insulation, its R-value plummets drastically, leading to massive energy loss. Water-soaked insulation may also require full removal due to building code implications.
- ASTM C518 Standard: Professional testing to assess R-value is typically done using standards like ASTM C518 with a heat flow meter (HFM) to provide accurate measurements. If you have concerns about your insulation, consider taking samples for testing. You can read more about this scientific look at hail-dented insulation on the Haag Global website.
How Hail Damage Compromises Your Roof’s Longevity and Structure
TPO roofing hail damage doesn’t just present immediate problems; it significantly impacts the roof’s long-term health and structural integrity.
- Accelerated Aging: Every hail impact, even if it doesn’t cause an immediate leak, creates a stress point. These micro-fractures and weakened spots become more vulnerable to daily thermal expansion and contraction, leading to premature material fatigue and degradation.
- UV Degradation at Impact Sites: When hail impacts damage the top protective layer of the TPO membrane, it exposes the underlying material to harsh UV rays. This accelerates the breakdown of the membrane, making it brittle and prone to further damage.
- Compromised Seams Leading to Leaks: TPO roofs rely on strong, heat-welded seams for watertight integrity. Hail impacts, even near seams, can stress these critical bonds. Over time, these compromised seams can begin to separate, creating insidious leak paths that are difficult to detect until water stains appear inside your building.
- Saturated Insulation Losing Structural Support: Water infiltration due to hail saturates the insulation, causing it to lose not only its thermal value but also its structural rigidity. It can become soft, squishy, or even collapse, creating uneven surfaces and ponding water areas that further exacerbate roof deterioration.
- Potential for Deck Rot or Corrosion Over Time: Water that penetrates the membrane and insulation eventually reaches the roof deck. For wooden decks, this leads to rot and decay, weakening the entire roof structure. For metal decks, it causes corrosion, compromising the deck’s integrity. Both scenarios can necessitate expensive and extensive repairs or even a full roof replacement.
TPO vs. The Competition: A Hail Resistance Showdown
Choosing a roofing material for your commercial property involves weighing many factors, and hail resistance is certainly one of them, especially in regions like Northwest Arkansas. Let’s see how TPO stacks up against other common flat roofing materials and explore factors that can weaken a TPO roof’s defenses.
How TPO Stacks Up Against Other Flat Roofing Materials
Each material has unique properties that dictate its hail performance.
- TPO (Thermoplastic Polyolefin): TPO membranes are generally more hail-resistant than smooth surface built-up roofs. Their flexibility allows them to absorb impact energy better than some other materials. TPO membranes can resist damage from up to 1 3/4-inch hailstones.
- EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer): EPDM roof membranes can resist damage from up to 2 1/2-inch hailstones, making them capable of withstanding larger individual hail impacts before puncturing. However, some sources suggest that TPO’s overall flexibility can make it generally more hail-resistant in terms of absorbing and dissipating impact energy, even if EPDM handles larger single stones without a direct breach. EPDM can become more brittle with age, increasing susceptibility.
- Modified Bitumen (Mod-Bit): Modified bitumen roofs are generally more susceptible to damage from small hailstones, usually about 1 1/2 inches in diameter. They may crack or tear under severe hail, especially if the surface granules are displaced. Granule loss exposes the underlying asphalt to UV, accelerating degradation.
- Built-Up Roof (BUR): While not explicitly listed with hail resistance stats, BUR membranes are generally considered more resistant to hail than single-ply membranes due to their layered structure and gravel surfacing (which disperses impact energy). However, if gravel is displaced, the underlying asphalt can be damaged.
Here’s a simplified comparison:
| Material | Typical Hail Resistance (Stone Size) | General Performance Against Hail
Your Local TPO Roofing Experts in Northwest Arkansas
Don’t wait for a small leak to become a major problem. If you suspect your commercial roof has sustained hail damage, contact the experts at Heritage Roofing & Repair for a thorough and professional inspection. We proudly serve the Berryville, AR community and the surrounding Northwest Arkansas region.
Heritage Roofing & Repair
3458 Arkansas State Hwy 221, Berryville, AR 72616




